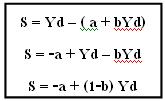1 National Income Determination
Theory of the national income is the relationship between the level of national income balance and Desired Aggregate Expenditure, DAE, as well as the effect of changes in demand and spending aggregates are to levels of employment and production factors, price levels in general. Lead to policies to solve problems or maintain employment, and target price levels as needed.
Economic equilibrium Aggregate Demand / AD = Aggregate Supply / AS.
The first important analysis of the national income, including aggregate demand (AD) consists of C + I + G + F (XM), respectively, consider the following.
1. Corruption Expedition / C
- Durable goods include the cost of consumer goods last for a long time, such as tables, chairs, furniture.
- Durable goods include the cost of consumer goods last for a long time, such as tables, chairs, furniture.
- Nondurable goods Include the cost of everyday consumer goods such as food.
- Services Including costs to acquire other services such as watching movies.
2. The factors that determine aggregate consumption and aggregate savings.
- Disposable Income / DI / Yd
- Changes in tax rates (t).
- Character of consumers (h)
- Social environment (So)
- Estimates of consumers (e)
-Consumer assets (A).
- Credits for consumption and interest rates (cr, I).
- Income distribution in society, (d).
3. Consumption Function
We use the word function (function) because the expenditure on consumption vary by income level shows that, after deduction of tax at…
C = cost to the consumer.
a = consumer spending, while income is equal to zero automation. Which do not depend on income (The need for human consumption. Even when there is no Y or S = 0).
b = inclination to spend on consumer income increased by 1 unit
(Marginal Propensity to Consume / MPC).
Y = national income (National Income).
a = consumer spending, while income is equal to zero automation. Which do not depend on income (The need for human consumption. Even when there is no Y or S = 0).
b = inclination to spend on consumer income increased by 1 unit
(Marginal Propensity to Consume / MPC).
Y = national income (National Income).
The average tendency in consumption and the tendency of the last unit of consumption
- Average Propensity to Consume / APC Refers to the tendency for people to spend money for consumption from existing levels.
APC= C/Yd
- Marginal Propensity to Consume / MPC Refers to the relationship between income and consumer spending. When people are changed to 1 unit of income consumption spending will change the vernacular. This is the ratio between changes in consumption spending to changes in income.
Due to MPC = b = slope of a line of customers.
= D C D/ Yd
Therefore, b is the inclination of consumers with the last unit.
** The Saving **
remainder of the cost to consumers of Pop on a number of Yd.
** Factors that determine Savings**
** The Saving Function**
Yd = S + C.
Therefore, S = Yd - C (1).
C = a + bYd.
Therefore, S = Yd - C (1).
C = a + bYd.
Substitute C in (1)
By-a savings in the past is used in consumption. On income in the hands person = 0.
Relationship between S and Yd, like C is S a Yd
** The Average Propensity to save**
is the ratio between savings and income.
APS = S / Yd
APS = S / Yd
** The Marginal Propensity to Save / MPS**
is the ratio of savings to changes in income changes. This will give answers that Whenpeople are changed one unit saving changes to the vernacular.
MPS = D S/DYd
Or MPC = (1 - b)
MPS = D S/DYd
Or MPC = (1 - b)
Picture shows the APC and MPC analyzed by graph
APC at the point A = AE / OE
APC at the point B = BF / OF
APC at the point B = BF / OF
MPC at the point A = B = BD / AD.
Due to Yd = C + S, if I always will be divided Yd.
Yd / Yd = C / Yd + S / Yd.
Is 1 = APC + APS.
Due to D Yd = D C + D S D Yd, if anyone will be divided over.
D Yd / D Yd = D C / D Yd + D S / D Yd.
Is 1 = MPC + MPS.
Due to Yd = C + S, if I always will be divided Yd.
Yd / Yd = C / Yd + S / Yd.
Is 1 = APC + APS.
Due to D Yd = D C + D S D Yd, if anyone will be divided over.
D Yd / D Yd = D C / D Yd + D S / D Yd.
Is 1 = MPC + MPS.
**The relationship between the tendency of consumers and tendency of savings**.
In the diagram (A) and (B) has the following observations.
Study the behavior of consumers according to the rules on short-term consumption of Keynes as we have studied since the beginning. Can be summarized as follows.
1. APC and the MPC will increase in proportion with the decrease on when revenue grew. Consumption will increase because the ratio is less than the income increase of APS, MPS will be much higher when income increases.
2. APC + APS = 1 always means that our revenue will be consumed before a broken part. The remaining savings are.
3. MPC + MPS = 1 always means D Y = D C + D S.
4. MPC (lower) (curved lines and consumption is down) and MPS (increase) when Yd (add) Q D C <D Y.
5. 0 <MPC <1.
6. 0 <MPS <1.
1. APC and the MPC will increase in proportion with the decrease on when revenue grew. Consumption will increase because the ratio is less than the income increase of APS, MPS will be much higher when income increases.
2. APC + APS = 1 always means that our revenue will be consumed before a broken part. The remaining savings are.
3. MPC + MPS = 1 always means D Y = D C + D S.
4. MPC (lower) (curved lines and consumption is down) and MPS (increase) when Yd (add) Q D C <D Y.
5. 0 <MPC <1.
6. 0 <MPS <1.
**Investment**
Investment in the economic meaning. "Expenditure in a period of time to buy a New fixed capital goods ,such as factory ,machinery ,housing, office ,building this includes changing the amount of raw materials and inventory. "
\ investment or to provide a replacement value of capital. The depreciation to other words.
Gross Investment = Net Investment + Replacement Investment
It = I nt + I rt
Buying shares on the Stock Exchange, Purchase of land for fear profit ,Buying second-hand assets and securities. In the calculation of national income is not considered an investment expense ,but it is a Financial Investment property purchases are not made equity assets in the economy. Were increased. Therefore, no effect on product direct the economy.
** Factor determining investment**
function of investment
I = f (Yd, A, B, C, D).
I = volume of investment.
Yd = income in cash.
B = net profit is expected to receive
A = rate of interest
C = the progress of technology.
Nature of investment
1. Autonomous Investment D investment by Yd line I parallel to the horizontal axis, which is measured by Yd.
Ia, most of the government investment, which does not profit directly, such as return on investment in education investment building roads.
2. Induced Investment
Things define investment
Investment decisions will need to compare the returns of interest and called the Marginal Efficiency of capital / MEC.
If I <IRR = or MEC investment.
I> IRR or MEC suspended their investment.
I> IRR or MEC
Such as S = R1/(1+i) + R2/ (1+i)2+ ... + Rn/(1+i)n
S = (Supply Price)
R1, R2, ..., Rn = annual revenue arising from the use of capital assets.
i = MEC.
If MEC> or = market investing.
If MEC <M / tab stop investment market.
i = MEC.
If MEC> or = market investing.
If MEC <M / tab stop investment market.
**Acquisition capital asset unit MEC (decrease)**
Revenue (increase) on the unit after the other assets <receipts (increase) Note the use of the asset first unit ,but productivity less than.
**Other factors that influence investment**